10.1 The Concept of Array
In this lesson, we shall learn how to work with a group of variables. A group of variables of the same data type is know as array
in Visual Basic 2015 . In working with a single item, we only need to
declare one variable. However, in dealing with multiple items of similar
type, we need to declare an array of variables. For example, it is very
tedious and time consuming to declare one hundred different names . To
fix the issue, we declare only one array to store those names. We
differentiate each item in the array by using subscript, for example,
name(1), name(2),name(3) …….etc.
A two dimensional array is a table of items that is
made up of rows and columns. The way to reference an element in a one
dimensional array is ArrayName(x), where x is the index or position
number of the element. The way to reference an element in a two
dimensional array is ArrayName(x,y) , where (x,y) is the index or
position number of the element. Usually it is sufficient to use one
dimensional and two dimensional array ,you only need to use higher
dimensional arrays if you need to deal with more complex problems. Let
me illustrate the the arrays with tables.
10.2 Dimension of an Array
In Visual Basic 2015, an array can be one dimensional or multidimensional. One dimensional array is like a list of items or a table that consists of one row of items or one column of items.Table 10.1: One Dimensional Array
| Student Name | Name(0) | Name(1) | Name(2) | Name(3) | Name(4) | Name(5) | Name(6) |
Table 10.2: Two Dimensional Array
| Name(0,0) | Name(0,1) | Name(0,2) | Name(0,3) |
| Name(1,0) | Name(1,1) | Name(1,2) | Name(1,3) |
| Name(2,0) | Name(2,1) | Name(2,2) | Name(2,3) |
| Name(3,0) | Name(3,1) | Name(3,2) | Name(3,3) |
10.2 Declaring Arrays
We can use Public or Dim statement to declare an array just as the way we declare a single variable. The Public statement declares an array that can be used throughout an application while the Dim statement declare an array that could be used only in a local procedure or module.The statement to declare a one dimensional array is as follows:
Dim arrayName(n) as dataType
where n indicates the last index in the array. Please note that n does not indicate the number of elements in the array, it is one less than the number of elements (n-1) because the first element is always the zeroth element. The first element is arrayName(0), the second element is arrayName(1), the third element is arrayName(2) and so on. The number of elements in an array is also known as length, we can retrieve the length of an array using the syntax arrayName.length
For example,
Dim CusName(10) as String
will declare an array that consists of 11 elements starting from CusName(0) through to CusName(10)
To find out the length of the array, you can write the following code:
Example 10.1
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim CusName(10) As String
MsgBox(CusName.Length)
End Sub
Running the program will produce a message box that displays the length of the array i.e 11, as shown in Figure 10.1

Figure 10.1
You might also declare an array with a non-zero starting index buy initialize an index value other than zero, as follows:Dim arrayname As DataType()
arrayName=New String(){1,2,3,….,n)
This array will consists of n elements, starting with arrayName(1)
Example 10.2
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim CusName As String()
CusName = New String() {1, 2, 3}
MsgBox(CusName.Length)
End Sub
The message box will display the length as 3
The statement to declare a two dimensional array is as follow:
Dim ArrayName(m,n) as dataType
where m and n indicate the last indices in the array. The number of elements or the length of the array is (m+1)x(n+1)
Example 10.3
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim CusName(5,6) As String
MsgBox(CusName.Length)
End Sub
Running the program and the message box will display a length of 42, as shown in Figure 10.2
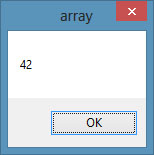
Figure 10.2
Example 10.4Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim num As Integer
Dim CusName(5) As String
For num = 0 To 5
CusName(num) = InputBox(“Enter the customer name”, “Enter Name”)
ListBox1.Items.Add(CusName(num))
Next
End Sub
This program will prompt the user to enter names in an input box for a total of 6 times and the names will be entered into a list box, as shown in Figure 10.3 and Figure 10.4
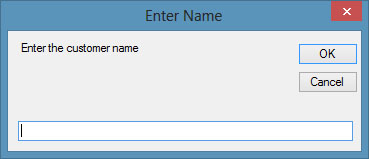
Figure 10.3

Figure 10.4
No comments:
Post a Comment